Integrating Terraform with HashiCorp Vault to manage static secrets
One challenge that comes up when provisioning resources over a cloud using Terraform is that you will need some form of credentials to log into the cloud or to access those resources. You don’t want to store those credentials inside your code, especially if you check your code into a versioning control system (VCS) for obvious reasons.
Even if you would provide Terraform with your credentials in a secure way, like the secure variable store (terraform.tfvars), it will most likely be the case that they end up somewhere inside the state file.
We can use HashiCorp Vault to manage secrets and integrating it with Terraform is a secure way to handle sensitive information.
Store Secrets in HashiCorp Vault
Sign in to Vault using Vault token.
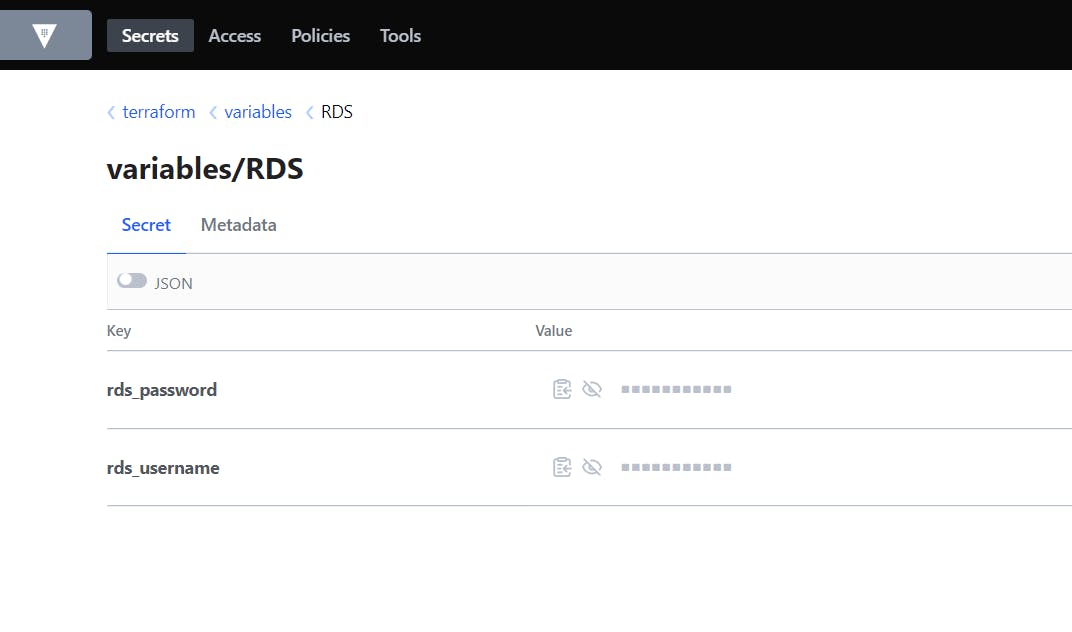
Enable a KV Secrets Engine under Secrets. Define the path and store your secrets under that path. In this example, my rds username and password are stored under "terraform/variables/RDS".
Now, to use static secrets stored in HashiCorp Vault in your Terraform code, you can use following method.
Authentication using Vault token
Set up the Vault Provider: First, you need to configure the Vault provider in your Terraform code. The Vault provider allows Terraform to communicate with HashiCorp Vault.
provider "vault" { address = "https://your_vault_url.com" }Authentication: Terraform needs to authenticate with Vault to access the secrets. There are several ways to authenticate, including using a token, an AppRole, or Kubernetes authentication. Let's use the token method in this example.
2.1. Obtain a Vault token: You will have a Vault token once you have configured Vault. You can also generate a Vault token manually.
2.2. Set the token in Terraform: Export the Vault token as an environment variable or set it directly in your Terraform configuration.
provider "vault" { address = "https://your_vault_url.com" skip_tls_verify = true token = "your_vault_token" }Accessing Secrets: Now that Terraform is authenticated with Vault, you can access secrets by using the
vault_generic_secretdata source.For example, let's say you have a secret named "RDS" with username and password stored in Vault.
data "vault_generic_secret" "rds" { path = "terraform/variables/RDS" } resource "aws_db_instance" "this" { for_each = local.rds_db identifier = each.value.name engine = each.value.engine engine_version = each.value.engine_version instance_class = each.value.instance_class allocated_storage = each.value.allocated_storage username = data.vault_generic_secret.rds.data.rds_username password = data.vault_generic_secret.rds.data.rds_password vpc_security_group_ids = var.vpc_security_group_ids db_subnet_group_name = aws_db_subnet_group.this[each.value.name].id availability_zone = var.availability_zone multi_az = var.multi_az publicly_accessible = var.publicly_accessible tags = merge( { "Name" = format("%s", each.value.name) }, var.tags ) }In this example, we're using the Vault provider to access the secret at the path "terraform/variables/RDS" and extracting the username and password from it. These values for username and password can then be used in the AWS DB instance resource.
Apply Terraform: When you run
terraform apply, Terraform will read the secrets from Vault and populate them into your infrastructure code.